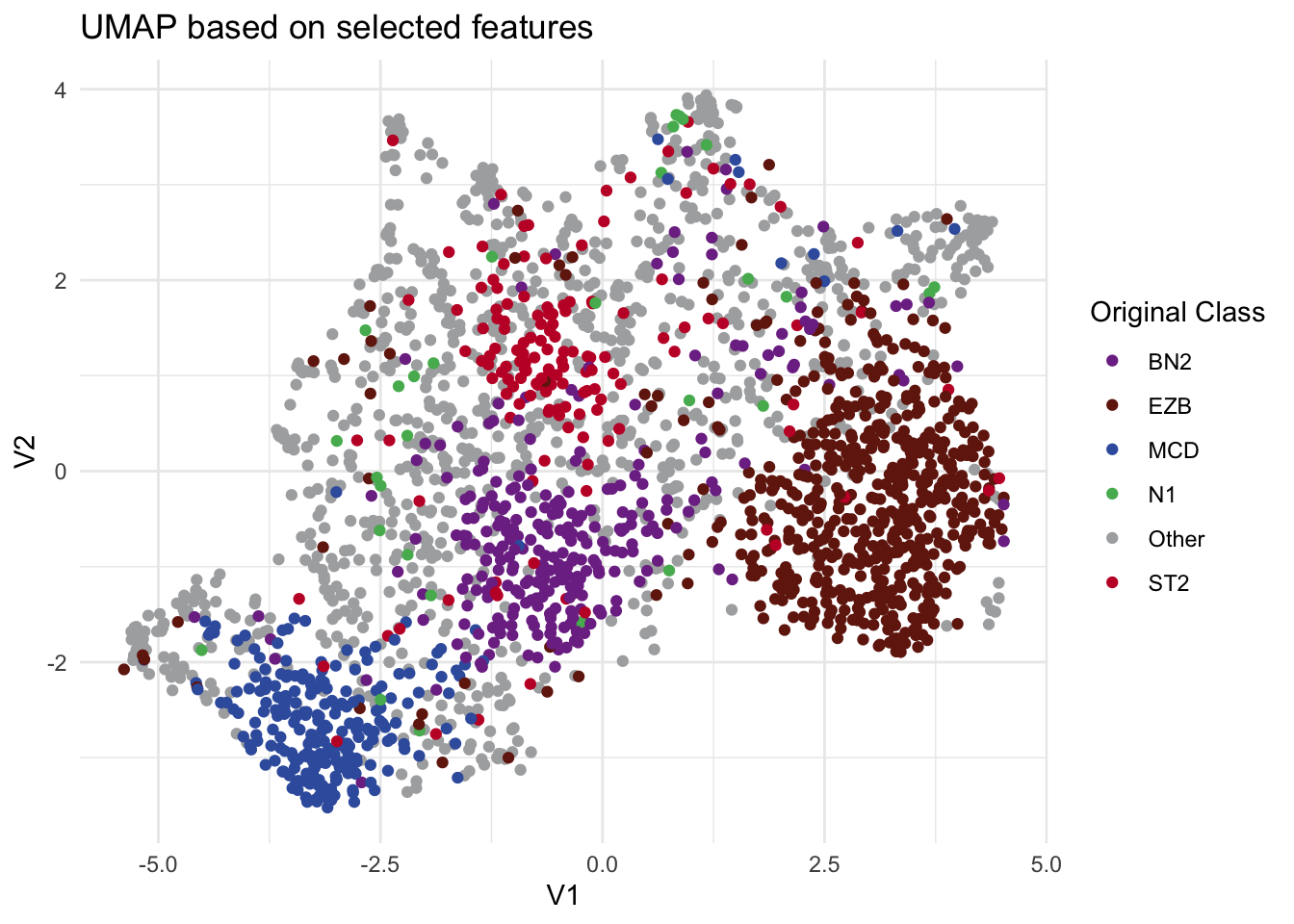
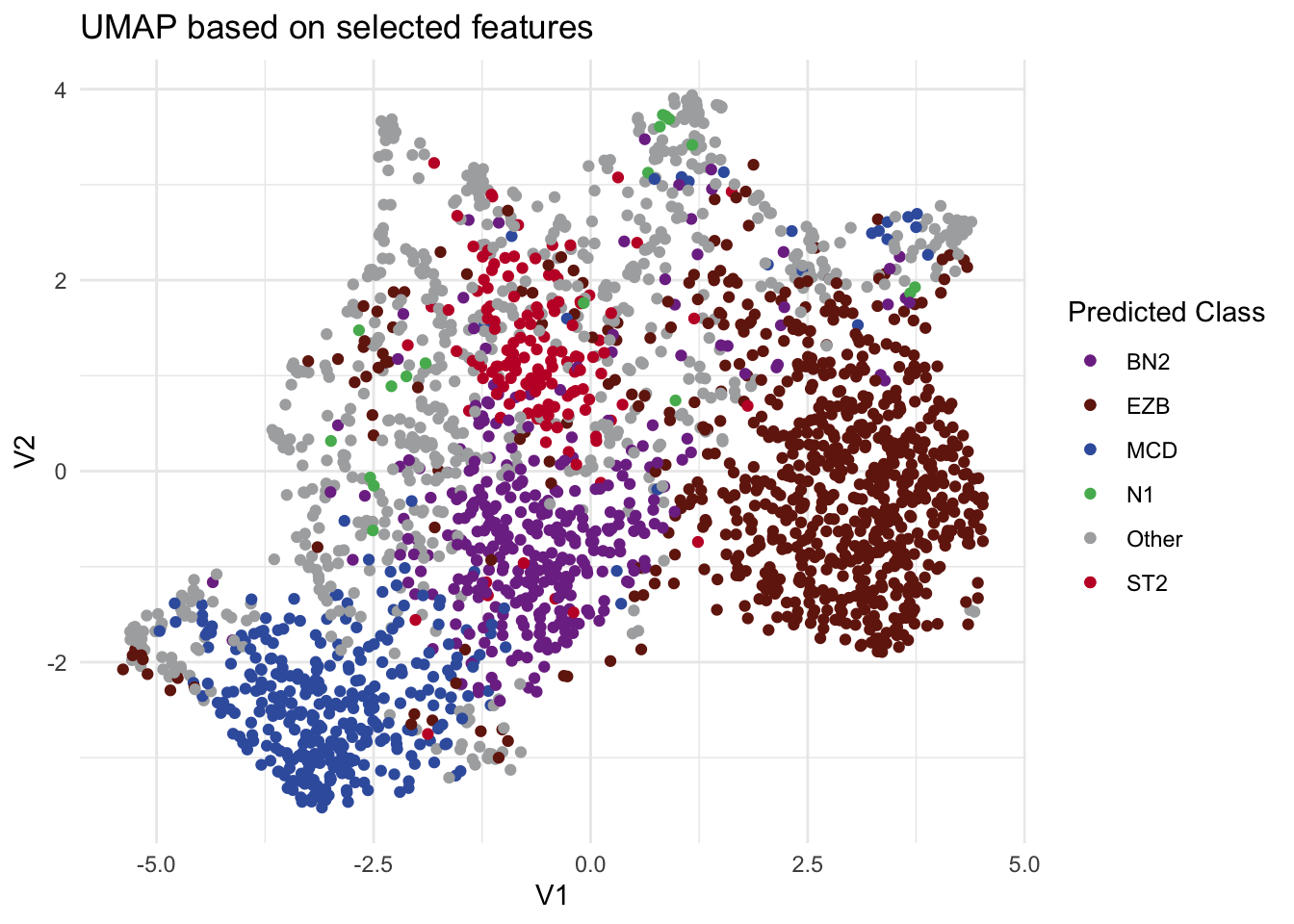
To demonstrate that our approach also works in the original high-dimensional feature space as well as UMAP space, we provide two additional functions: DLBCLone_KNN and DLBCLone_KNN_predict. Unlike the earlier functions, these do not rely on UMAP embeddings. Instead, they call UMAP only to compute pairwise distances in the high-dimensional space, a preliminary step in the UMAP algorithm before applying KNN directly. It’s important not to confuse these with the previously introduced DLBCLone functions, which embed the data in a lower-dimensional space and run KNN on those embeddings. With the earlier functions, users never need to handle the KNN step themselves, since it is built into the workflow. These are not meant for production usage!
DLBCLone_KNN
Weighted KNN on a feature (mutation) matrix with optional upweighting of user-specified “core” features, optional exclusion of “hidden” features, and optional optimization of an explicit outgroup (e.g. “Other”).
features_df matrix (rows = samples, cols = features) rownames must be sample IDs
metadata data frame with at least sample_id and the ground-truth label column given in truth_column
core_features character vector of feature names to upweight (optional)
core_feature_multiplier numeric multiplier for core_features (default: 1.5)
hidden_features vector of feature names to drop
min_k integer K range to explore when optimizing (default: 5)
max_k integer K range to explore when optimizing (default: 60)
truth_column name of metadata column with ground-truth class labels
truth_classes vector of all classes to consider (including other_class if you intend to optimize for it)
other_class name of the explicit outgroup class (default: “Other”)
optimize_for_other if TRUE: computes a separate “other” score (ratio) and searches a purity threshold; if FALSE, treats all classes symmetrically
predict_unlabeled if TRUE: re-runs KNN to classify samples that were present in features_df but not in metadata
plot_samples optional vector of sample_ids to keep in example plots
DLBCLone_KNN_out optional prior result; if supplied, its learned parameters are reused (skip optimization)
epsilon small value added to distances before weighting
weighted_votes If FALSE: neighbors are unweighted (equal votes)
skip_umap If TRUE: skip layout optimization plots at the end
dlbcl_knn <- DLBCLone_KNN(
features_df = best_opt_model_matrix,
metadata = dlbcl_meta_clean,
min_k = 5,
max_k = 21,
optimize_for_other = TRUE
)
knitr::kable(head(dlbcl_knn$predictions))
| 00-14595_tumorC |
25.7028 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
EZB |
25.7028 |
EZB |
25.7028 |
Inf |
EZB |
16.5 |
EZB |
EZB |
EZB |
| 00-15201_tumorA |
2.3604 |
0 |
2.0548 |
4.2871 |
0 |
14.8873 |
MCD |
4.2871 |
MCD |
4.2871 |
0.288 |
Other |
16.5 |
MCD |
MCD |
Other |
| 00-15201_tumorB |
0 |
6.0352 |
0 |
3.5092 |
0 |
13.1948 |
BN2 |
6.0352 |
BN2 |
6.0352 |
0.4574 |
N1 |
16.5 |
BN2 |
BN2 |
Other |
| 00-17960_CLC01670 |
29.3236 |
3.1066 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
EZB |
29.3236 |
EZB |
29.3236 |
Inf |
EZB |
16.5 |
EZB |
EZB |
EZB |
| 00-22011_tumorB |
4.3219 |
0 |
0 |
4.1948 |
0 |
16.0209 |
EZB |
4.3219 |
EZB |
4.3219 |
0.2698 |
Other |
16.5 |
EZB |
EZB |
Other |
| 00-23442_tumorA |
27.5503 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
8.411 |
EZB |
27.5503 |
EZB |
27.5503 |
3.2755 |
EZB |
16.5 |
EZB |
EZB |
EZB |
DLBCLone_KNN_predict
Applies a previously optimized DLBCLone_KNN model to predict class labels for new (test) samples. This function combines the training and test feature matrices, ensures feature compatibility, and uses the parameters from a DLBCLone KNN optimization run to classify the test samples. Optionally, runs in iterative mode for more stable results when predicting multiple samples. DLBCLone_KNN_predict is only reproducible when you run a sample through individually because the other samples affect the nearest-neighbor distances. It is OK for when users want to “try out” a model but it doesn’t scale well, predict_single_sample_DLBCLone is the way to go.
train_df matrix of features for training samples (rows = samples, columns = features)
test_df matrix of features for test samples to be classified
metadata data frame with metadata for all samples, including at least a sample_id column
core_features optional character vector of feature names to upweight in the KNN calculation
core_feature_multiplier multiplier to apply to core features (default: 1.5)
hidden_features optional character vector of feature names to exclude from the analysis
DLBCLone_KNN_out output from a previous call to DLBCLone_KNN containing optimized parameters
mode if “iterative”, runs KNN prediction for each test sample individually (recommended for stability)
Batch Mode
predictions_b <- DLBCLone_KNN_predict(
train_df = best_opt_model_matrix,
test_df = valid_df,
metadata = dlbcl_meta_clean,
DLBCLone_KNN_out = dlbcl_knn,
mode = "batch"
)